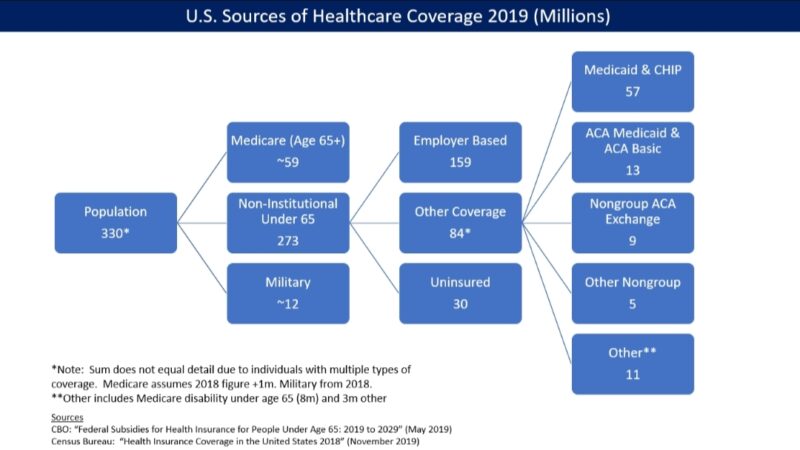
Health insurance in the United States plays a critical role in protecting individuals and families from high medical costs. Unlike many countries with universal healthcare systems, the US relies on a combination of private insurance, employer-sponsored plans, and government programs.
Understanding how health insurance works in America is essential, especially for residents, immigrants, self-employed workers, and retirees who want to avoid unexpected medical expenses.
In the US healthcare system, health insurance helps cover costs such as doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription drugs, preventive care, and emergency treatment. Without insurance, even routine medical services can be extremely expensive.
For this reason, most Americans rely on insurance plans either provided by employers, purchased privately, or supported by government programs designed for specific groups.
One of the most important public programs is Medicare, which primarily serves people aged 65 and older, as well as certain individuals with disabilities. Medicare is divided into several parts, covering hospital care, medical services, and prescription drugs.
While it significantly reduces healthcare costs for seniors, many beneficiaries still choose supplemental plans to cover gaps in coverage.
Another major pillar of the US healthcare system is the Affordable Care Act, commonly known as Obamacare. This law expanded access to health insurance through online marketplaces, subsidies, and protections for people with pre-existing conditions. ACA-compliant plans are required to cover essential health benefits, making them a popular option for individuals and families without employer-sponsored insurance.
Private health insurance remains the most common form of coverage in the United States, often provided through employers. Large insurers such as UnitedHealthcare, Blue Cross Blue Shield, Aetna, and Cigna dominate the market. These companies offer a wide range of plans with different premiums, deductibles, and provider networks, allowing consumers to choose coverage that fits their medical needs and budget.
The cost of health insurance in America varies widely depending on age, location, income, and type of plan.
Monthly premiums can range from a few hundred dollars to well over a thousand dollars for comprehensive family coverage. In addition to premiums, policyholders must consider deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance, which can significantly impact total healthcare spending over the course of a year.
For people without access to employer-sponsored plans, individual and family health insurance purchased through the ACA marketplace is often the best option. These plans may qualify for income-based subsidies that lower monthly premiums and out-of-pocket costs. Self-employed individuals, freelancers, and gig workers commonly rely on marketplace coverage or private insurers to meet their healthcare needs.
Choosing the best health insurance plan in the United States requires careful comparison of coverage benefits, network size, and total costs. Consumers should evaluate whether their preferred doctors and hospitals are included, how prescription drugs are covered, and what the maximum out-of-pocket limits are. A well-chosen plan not only provides financial protection but also ensures access to timely and quality healthcare services.
Final Thoughts
Health insurance in the United States is complex, but understanding the available options can help individuals make informed decisions. Whether through Medicare, ACA plans, employer coverage, or private insurance, having the right health insurance plan is essential for long-term financial security and peace of mind in the US healthcare system.